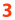Plastic Resin
Plastic resin refers to a type of polymer material that is used as a raw material in the production of various plastic products. Plastic resins are typically derived from petroleum or natural gas, and they undergo a process called polymerization to form long chains of molecules. These chains give plastics their unique properties, such as flexibility, rigidity, transparency, and durability.
Plastic Resin Types
Plastic resin is a viscous liquid that can be molded into various shapes when heated and then solidifies when cooled. Resins offered by GID Plastic, one of the most reliable plastic resin companies, are commonly used in the production of plastic products, such as bottles, containers, and packaging materials.
Surlyn
Surlyn is a versatile polymer material known for its excellent clarity, impact resistance, and chemical resistance. It is commonly used in packaging, automotive, and consumer goods industries for applications such as bottles, caps, and protective coatings.
EAA
EAA is a copolymer material that combines the properties of ethylene and acrylic acid. It offers excellent adhesion, heat sealability, and barrier properties. EAA is widely used in packaging, particularly for food and beverage containers, as well as in the automotive and electrical industries.
EEA
EEA is a copolymer material that combines the properties of ethylene and ethyl acrylate. It provides excellent flexibility, impact resistance, and low-temperature performance. EEA is commonly used in applications such as films, coatings, and adhesives.
POE
POE is a thermoplastic elastomer with excellent flexibility, impact resistance, and low-temperature performance. POE resin is widely used in automotive, footwear, and wire and cable industries for applications such as seals, gaskets, and insulation.
EVA
EVA is a copolymer material that combines the properties of ethylene and vinyl acetate. It offers excellent flexibility, impact resistance, and thermal stability. EVA is commonly used in footwear, sports equipment, and packaging industries.
BASF TPU
BASF TPU is a versatile polymer material known for its excellent mechanical properties, abrasion resistance, and chemical resistance. It is widely used in automotive, footwear, electronics, and industrial applications for components such as seals, gaskets, and coatings.
Advantages of Plastic Resin
Plastic resin offers several advantages that contribute to its widespread use in various industries and applications. Some of the key advantages include:
1. Versatility: Plastic resins come in a wide range of types and grades, offering versatility in terms of properties and applications. They can be molded into different shapes, sizes, and forms, allowing for customization and flexibility in product design.
2. Lightweight: Plastic resins are generally lightweight, which is advantageous in many industries such as automotive, aerospace, and packaging. The reduced weight can result in lower transportation costs, improved fuel efficiency, and easier handling and installation.
3. Durability: Plastic resins often exhibit excellent durability and resistance to wear, impact, weathering, and chemical exposure. This makes them suitable for applications that require long-lasting and robust materials, such as construction, automotive parts, and electronic enclosures.
4. Cost-effective: Plastic resin production is typically more cost-effective compared to other materials like metal or glass. Plastic resins are easily processed, allowing for efficient and high-volume manufacturing. The lower production costs can translate into more affordable end products for consumers.
5. Design freedom: Plastic resins offer tremendous design freedom due to their moldability. They can be molded into intricate and complex shapes, allowing for the creation of innovative and ergonomic designs. This flexibility plays a crucial role in industries like consumer goods, electronics, and medical devices.
6. Chemical resistance: Many plastic resins demonstrate excellent resistance to chemicals, which is advantageous in applications where material contact with corrosive substances is common. Chemical resistance allows for the safe storage and transportation of various substances, contributing to product integrity and safety.
7. Recyclability: Plastic resins can often be recycled and reprocessed into new materials, reducing waste and environmental impact. Recycling initiatives help divert plastic waste from landfills and conserve valuable resources, promoting a more sustainable approach to plastic usage.
FAQs of Plastic Resin
Q:
How can I identify the type of Plastic Resin used in a product?
1. Look for markings or symbols: Many plastic products have symbols or markings on them that indicate the type of resin used. These symbols are typically located on the bottom or back of the product and are known as resin identification codes. These codes consist of a number within a triangle of arrows (commonly referred to as the recycling symbol). Each number corresponds to a specific type of plastic resin, such as PET (1), HDPE (2), PVC (3), LDPE (4), PP (5), PS (6), and other plastics (7).
2. Perform a burn test: This method requires caution and should only be done if you are experienced and have proper safety precautions in place. By carefully burning a small section of the plastic, you can observe the characteristics of the flame, smell, and ash residue to help identify the type of plastic resin. For example, polyethylene (PE) burns with a blue flame, produces a waxy smell, and leaves a white ash.
3. Use specialty testing kits: There are specific testing kits available that can help identify different types of plastic resins. These kits typically involve using chemicals or solvents that react differently with each type of plastic. By performing tests according to the kit's instructions and observing the reactions, you can determine the type of plastic resin present.
4. Consult the manufacturer or product documentation: If you are unable to identify the plastic resin through markings, testing, or other methods, contacting the manufacturer or referring to the product documentation may provide the necessary information.
Q:
Are Plastic Resins recyclable?
Yes, many plastic resins are recyclable. However, not all plastics have the same recycling capabilities due to variations in their chemical properties and composition. It is important to understand and follow the recycling guidelines specific to your local recycling facilities.
Certain commonly recycled plastic resins include:
1. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET or PETE): This is commonly used in soda bottles, water bottles, and food packaging.
2. High-density polyethylene (HDPE): Found in milk jugs, detergent bottles, and some plastic bags.
3. Low-density polyethylene (LDPE): Used in squeeze bottles, plastic wraps, and garbage bags.
4. Polypropylene (PP): Found in yogurt containers, bottle caps, and some food containers.
5. Polystyrene (PS): Commonly used in foam packaging, disposable cups, and some food containers.
6. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC): Recyclability of PVC can be limited due to the presence of additives. However, some rigid PVC products can be recycled in specific recycling programs.
It is important to note that the recyclability and acceptance of plastic resins for recycling can vary by region. Some plastics, such as mixed plastics (#7) or plastics with multiple layers, may be less commonly accepted in recycling programs.
Location : No. 3, Nange 10 Road, Daojiao Town, Dongguan City, Guangdong Province, 523000 Dongguan,
Contact : com gidplastic, +86 13925704673